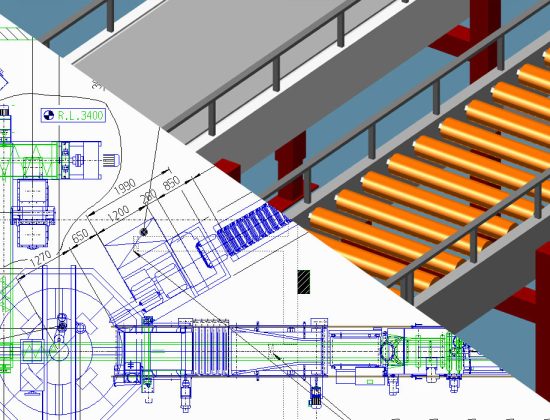
Plant design at a glance – individual sectors and trades explained in detail
What is plant design?
Plants are technical equipment consisting of several technical components that are interconnected in terms of process technology. They are used in almost every production or operating facility. The importance of plant engineering in industry and business is correspondingly high. Whether it is an automatic bandsaw for the wood industry, a conveyor belt for glass transportation or a heat exchanger for biogas production, all these examples are individual technical plants for the realisation of complex tasks. The design and realisation of plants is carried out by individual plant engineers.
With the help of plant design, technical industrial plants are realised after an extensive design process. This branch of industry is characterised by a high degree of complexity. The activities that have to be carried out for a finished plant at the customer’s site cover a very wide range: from ecological aspects to the manifold technical activities and an increasing scope of services.
In addition to environmental factors, a specialised plant manufacturer must also ensure the design of the equipment. The interconnection, optimisation and adaptation of technical components must be developed as a concept and considered as a process, which automatically requires a lot of experience on the part of a manufacturer. All the monitoring and control systems, as well as the supply and disposal equipment, which are all interlinked, create a finished plant.
Another major difference to regular industrial projects is that the processing of an order in plant design is usually a one-off project. Due to the individual specifications and tasks of a plant, it is clearly distinguished from the industrial mass production or batch production of a product. The deployment of personnel, the financial resources and also the time limits for the targets of a plant depend on the order.
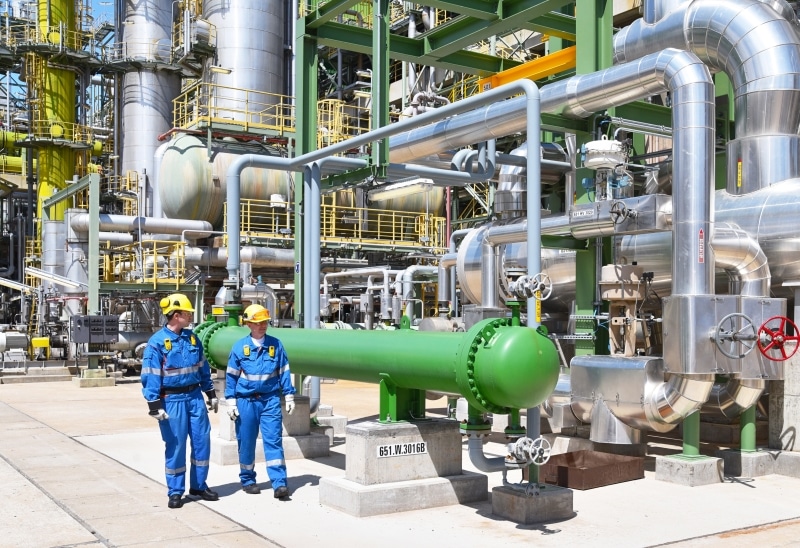

What is a plant?
A plant is, amongst other things, an energy production or industrial plant that is categorised both as a structural plant and as a technical plant. It is described as a combination of spatially related machines or devices that may be functionally linked to each other.
The difference between small and large plants
The object structure is based on different characteristics when constructing plants. In plant design, we speak of complete plants with partial plants and individual components. Complete plants are complex and interlinked plant systems that connect subsystems and components with each other in a process. The greater the number of subsystems and components, the higher the degree of complexity of the complete system.
A subsystem ia a part of a larger system together with its components. The subsystem is characterised by the fact that it functions as a self-contained system within the overall system. Subsystems can basically be classified into different disciplines. For example:

- Construction technology (e.g. building construction),
- storage, transport and conveyor technology (e.g. components geared towards logistics),
- the supply or disposal technology (e.g. power supply) or also
- process engineering or manufacturing technology (e.g. components of manufacturing technology).
Small plant design / special plant design

Small plant design and special plant design deal with the designing and construction of special plants that fulfil a task in small space or serve as a component of a larger plant. These plants are often delivered compactly in standardised containers. Small plants or special plants often also include plants for renewable energies, because biomass plants or wind power plants are also small self-contained systems.
For the renewable energy sector, CAD Schroer is currently offering a discount on the M4 PLANT software for plant design.
Find out everything about the special offer here >>
Components in plant design
The components in plant design are divided into individual elements and connecting elements. Individual elements are, for example, machines, apparatus, controls or pumps. Steel frames, pipelines or electric cables serve as connecting elements. For the purpose of differentiation, different types of installations can be defined or the installations can be assigned to specific disciplines and areas.
3D software for plant design
Detailed design and layout of your factory or plant in one integrated solution. Benefit from the advanced functionality and a great service.

In which industries is plant design used?
Due to its great importance, plant design is also referred to as the engine of the economy. Whether it is the food industry, the pharmaceutical industry, construction, aviation, environmental technology, plastics processing, printing, packaging, the building materials industry or the automotive industry, there are plant engineers for every industry that uses machines and plants. The following are examples of industries whose products and goods would be unthinkable without plant engineering.
Chemical plant design
Chemical plant design is currently enjoying a major upswing. Chemical products such as medicines, detergents, plastics, special chemicals or even high-tech products make life more comfortable. Completely coordinated and effective process engineering industrial plants ensure the optimal manufacture and production of chemical goods and substances. In the construction of chemical plants, pneumatic conveying systems or optimised control systems are often used. This can increase the yield of production for chemicals and chemical products. In the chemical industry, there is therefore a particular focus on mass production.
In a chemical plant, a synthesis developed in the laboratory is often produced first. However, this cannot be immediately transferred to the construction of a chemical plant, so that here special emphasis is placed on the so-called “scale-up”. In this process, the plant engineer has to deal with points such as the determination of the optimal reaction conditions or also the separation processes at an early stage. Cooperation with experts from chemical reaction technology is an important factor at this point and differs from the construction of plants from other industries. The construction of a chemical plant is cost- and time-intensive. In addition, safety-related framework conditions as well as ecological aspects have to be considered here. In addition, there are official and legal requirements, as well as legal factors that must be taken into account when building a chemical plant.
The company CEL International supports the pharmaceutical and process industry in all investment phases of plant design with distinctive expertise. CEL International plans process plants with M4 PLANT >>
Laboratory technology – small laboratories and plants
Laboratory technology can be considered as system and laboratory plant engineering, for example, for apparatus for mechanical and thermal separation of substances on a smaller scale. They often have cooling and heating systems or pressure and vacuum systems. Each customer uses a different plant for laboratory construction. These plants are often used for chemical process engineering applications. Therefore, there are many different requirements for the equipment. For example, they must be highly resistant to temperature, pressure and corrosive agents. In addition, the availability of accessories is also important for laboratory plants in order to be able to cover the widest possible range in process development. Furthermore, a successful plant manufacturer in this field must also be familiar with the development or manufacture of customised pressure equipment or chemical laboratory technology. In addition, measuring devices or digital data loggers and controls are often used in laboratory plant engineering.
Water treatment
Water treatment is also part of plant engineering. Along with oxygen, water is one of the most important elements on earth and a scarce commodity in many places in today’s world. Accordingly, water treatment is of great importance. Whether softening plants or service and drinking water treatment plants: water treatment is an important factor in everything from single-family homes to building services or even on ships. The tasks in the field of water treatment* are water extraction, conveyance, storage, treatment, distribution and also the optimisation of water quality.
* Water treatment plants Ovivo >>
Water treatment utilises a comprehensive process that has the goal of treating the water and must be taken into account when designing the plant. In the field of mechanical engineering, the plant constructor deals with components such as pumping stations, deep well equipment, metering shafts, distributors, pressure boosting systems, water towers, containers for drinking water, ozone systems, compressed air systems, sterilisation systems, dosing systems, piping systems or even deep wells. There are also components for energy recovery such as turbines and generators.
Plant engineering and its disciplines
Numerous technical disciplines converge in plant design, from process engineering to energy technology. Plant design uses various disciplines depending on the type of plant to be designed. Classic disciplines are process engineering, energy engineering, supply engineering, production engineering, mechanical engineering and electrical engineering.
Plant design is in itself a very diverse field of activity. The main focus in plant design is on energy technology with an emphasis on power plant design. Production facilities such as factories are another important area. In plant design, a distinction is made between the energy sector and production facilities.
Energy technology
The energy sector in plant design is dominated by power plants. Power plants are technical facilities for the generation of electricity. Electricity is generated from non-renewable or renewable energy sources. Non-renewable energy sources are obtained from finite raw materials, including crude oil, natural gas and coal. These are also referred to as fossil energy sources. Around the world, coal, for example, is burned in power plants (coal-fired power stations) and converted into electricity. Crude oil and natural gas can also be used to generate electricity.
In combined cycle power plants (CCPP), the fuel is burned in the combustion chamber of the gas turbine, which then drives a generator.

In combined heat and power (CHP) plants, not only is electricity generated, but the heat is also used. Small CHP plants work with a combustion engine.
Renewable energies such as wind, solar and biomass are together by far the most important energy source for electricity generation. Renewable energies include tidal power plants, water storage power plants, geothermal power plants (geothermal energy) as well as photovoltaic, wind power and biomass plants.
Current discount promotion for renewable energies, discount on the M4 PLANT software for plant engineering >>
Production engineering
Production engineering is a classic specialist area in plant engineering. Production engineering deals with the technical, economic and organisational management of the industrial manufacturing of products. In factories, production processes are tailored to industrial needs. These can be production lines for vehicles, machines or plants for the production of food. The products within production engineering show a high degree of heterogeneity, because the spectrum of applications is very broad and ranges from mechanical components and systems to complete machines and plants. Mechanical and plant engineering is therefore the first port of call for industrial companies that want to further develop and optimise their production, technologies, processes or products.
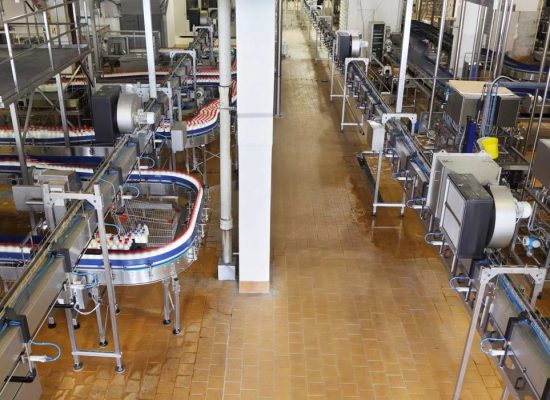

Today, companies must be able to manufacture products with customised functionality and at the same time meet the demands for increased performance and product durability with undiminished functional safety. In this context, the customisation of products is not directed at consumer goods in the classic sense, but refers to products such as machines, devices, etc. for mechanical and plant engineering. Despite the increased complexity, these should offer user-friendly and controllable interfaces for the respective user and help to overcome technology barriers. The use of material- and energy-efficient manufacturing processes and the associated shift of intelligence from the product to the manufacturing process are now both a unique technological selling point and an economic necessity for producers.
Process engineering
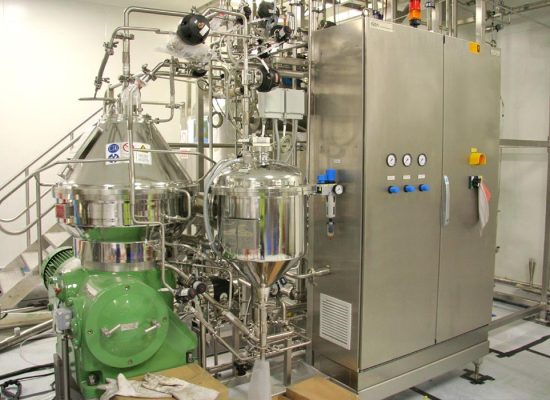
In plant design, especially in process plant engineering, almost everything revolves around oil and gas. These resources have to be extracted, cleaned and processed for further use and then transported to consumers as intermediate or end products. Process engineering plants consist of apparatus, machines and pipelines, and enable the manufacture of a wide range of products that have become indispensable in our lives.
Process engineering design: Modern software supports process engineering design by creating design documentation in the form of intelligent piping & instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs).

Offshore or onshore plant design
The first distinguishing feature in plant design is limited to whether the plant is built on land or on water. This is because plants are not only built on solid ground, but also at sea. Therefore, a distinction is made between offshore (e.g. at sea) and onshore (on land) plants.
Offshore facilities
“Offshore” means “off the coast”. In plant design, offshore means the construction and installation of plants on the open sea. The most common types of offshore installations are oil drilling rigs and installations that use renewable energies such as wind or tides. Offshore wind farms usually consist of a very large number of wind turbines in shallow coastal waters.
Onshore facilities
“Onshore” stands for “on land”. In the field of wind power, onshore wind farms mean clusters of wind power plants for generating energy on the mainland, and has the great advantage that the construction of the turbines is much cheaper than with turbines at sea.
Plant design disciplines
In plant design, there are different disciplines that are successfully used for various industries and sectors. The most important disciplines are briefly listed below.
Building design
Building design in plant design is an important key to the implementation of sustainable and resource-saving building technology. In today’s world, saving energy is an important point that must be adhered to early in the design process. The objectives and legal requirements for buildings are becoming ever more stringent. In building design, systems are therefore used that focus particularly on these points, but at the same time must take into account the functionality and purpose of the building and the needs of the occupants or employees.
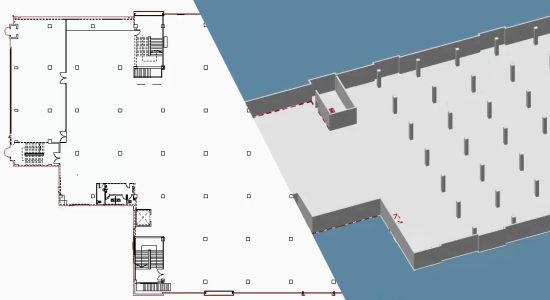
Examples of systems are central air-conditioning systems, heating technology, lifts, escalators or even digitalisation and the interaction of components in the building. The special feature of building design in plant design is primarily that the target matrix in the development process sometimes has contradictory goals (e.g. use of the building contrary to resource conservation) and is therefore very complex. CAD Schroer offers practical solutions here in the field of building design and is familiar with the entire design processes.
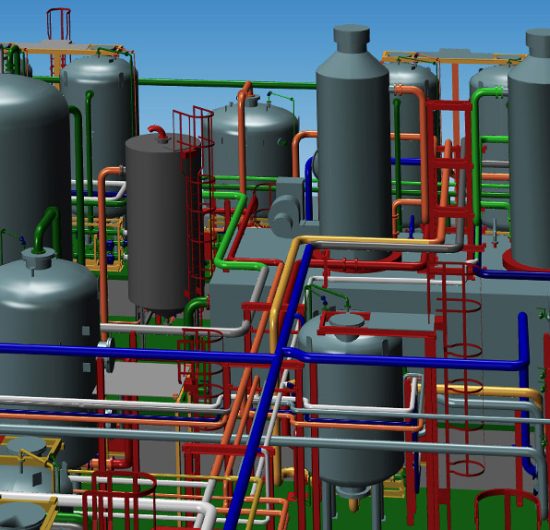
Layout design
Layout design in plant design takes into account various components of plants (e.g. machines or apparatus), which are arranged according to design considerations. Main influencing factors come from the field of process engineering, but also from authorities or the plant operator. The main documents in plant design are so-called plot plans (overall layout plan), as well as various layout plans. The plot plan is a key document and is used to position the individual parts of the plant. It is also used in the early design phase to mark and identify tie-in points. By means of the layout plan, different views (side view, top view and sections) can be shown. The installation of machines and structures can also be identified and provided with dimensions.
Layout plans can be conveniently created in 2D or 3D with the M4 PLANT software for plant engineering, and all required drawings and sectional views can be generated. Learn more about M4 PLANT >>

Piping Design
Piping Design deals with the design and construction of pipelines and pipeline systems and is one of the most important trades in plant design. These can be used to transport substances such as water or wastewater, but also gases and liquids such as fuel oil. In addition, there is a great focus on pipeline construction in the field of district heating supply. Clients come from the municipalities and utilities sector, but also from the chemical industry. The construction of plants in the field of pipeline construction not only deals with pipe systems and pipelines, but also with special features such as civil engineering or structural engineering. Pipelines can usually be laid underground or above ground. In the chemical industry, a pipe bridge is used for the most part in the construction of plants, while in hydraulic engineering or district heating supply, an underground system is predominantly used.
Steel design
Steel design is a central discipline in plant design and is classically concerned with steel girders, pipes or also sheet metal, which are connected to a supporting structure with connecting elements such as screws or also by welding. An important element in steel construction is a gusset plate, which connects various bars in the supporting structure. Steel construction also deals with elements such as concrete (e.g. reinforced concrete) and also the steel frame construction.
Steel construction includes metal construction solutions for industry, building construction, plant design and apparatus engineering such as stages, stairs, railings or steel constructions for machines. The design cycles are rather short compared to other disciplines. On the other hand, a complex plant in steel construction requires a high degree of precision in the area of manufacturing the plant components so that the individual components fit together perfectly when the finished plant is assembled.

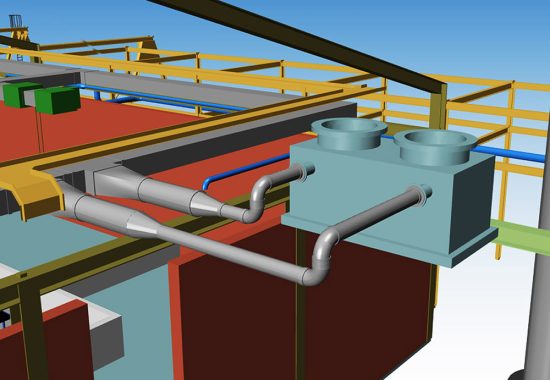
Ventilation technology
Ventilation technology is used to supply technical processes or also building structures such as operating rooms with air. A certain air quality must be maintained and guaranteed by the ventilation system. Systems for room air technology and also for process air technology ensure the performance of various tasks such as the separation, drying and also the conveyance of air for technical purposes. Air-conditioning systems control temperature and humidity. For all elements of ventilation technology, the system builder must observe and comply with various standards and regulations.
Refrigeration
When you go shopping for food from the freezer, you always expect high and particularly fresh quality. Until a food item, be it vegetables or fish, reaches the table, it must always remain fresh and continuously frozen. To ensure this, the first step starts quite early in the deep-freeze chain. As a supplier of compressor systems which utilise Howden screw compressors, the Italian-based company CO-REF Srl makes a substantial contribution to safe refrigeration. High-quality compressor systems for the refrigeration and freezer industry are designed by CO-REF Srl with M4 PLANT >>
Read also how companies from the refrigeration industry use M4 PLANT for plant design >>

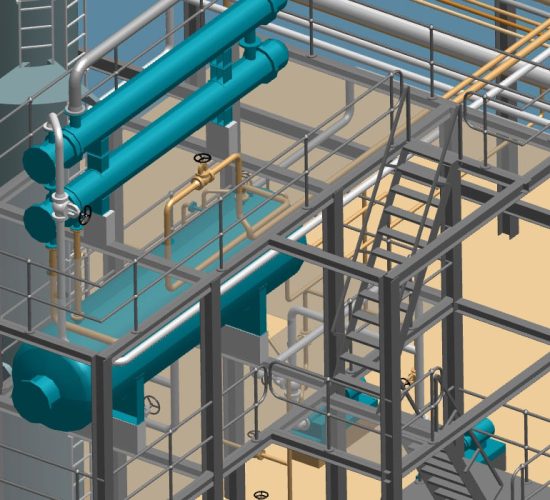
Cable trays
Cable trays are the paths along which cables are laid in a facility. In contrast to self-supporting pipelines, the rather “soft” cables require a guide and support system in order to be laid in an orderly manner through a facility or building. Cable trays carry cables of all kinds, which include e.g. power, signal or telecommunication lines. One of the main aspects of cable trays, which a successful plant constructor must also focus on, is the economic efficiency in the construction of a plant or cable tray.
The design of cable routes often seems to be overlooked in plant design. The main focus of plant design tends to be on the pipelines or other disciplines. The disciplines associated with cable route design are heating, air-conditioning and ventilation design (HVAC for short) as well as piping design. In addition, there is also building and installation design, steel construction and overall multi-disciplinary system design. From the list of the different numbers of disciplines, it can be assumed that there is sometimes great potential for physical interference between the disciplines.
Cable route design is a classic field for interference problems, because this is where the plant designer meets the concerns of the electrical installation. The range of skills required by a modern cable route design is broad and includes that of a 3D CAD specialist, plant designer, mechanical, steel construction, civil and electrical engineer, database specialist, interface coordinator and purchaser. Plant engineering covers many areas, and in order to create an interference and collision-free plant design, an intelligent design system with integrated collision control and consistency checking is necessary, such as CAD Schroer’s M4 PLANT software.
The image below shows an example of 3D design of a plant component. The incoming cable tray and the connecting pipelines are clearly visible, the individual components are shown schematically in their basic dimensions for the purpose of collision detection and are shown in both detail and to scale.

The life cycle of a plant
The life cycle of a plant is measured in years or decades. Every plant requires ongoing maintenance and may be subject to significant changes or innovations over time. All types of plant, whether they are in industrial plants, commercial buildings or hospitals, sewage treatment plants, schools or infrastructure projects, all need to be designed, built, operated, maintained and eventually, decommissioned.
Plant engineers who want to successfully meet the demands of a dynamic world need technologies that enable them to design innovative, individual plant design projects faster, more accurately and more profitably. The construction of plants involves different areas, and CAD Schroer’s M4 PLANT software is used for the detailed design of plants.
Complete plants (plant systems)

One of the key aspects of plant design is to combine technical components into a predefined and functional overall system whose tasks have been specified beforehand.
Complete plants are entire plant systems that integrate various technologically connected subsystems and components. Only the correct interaction of all subsystems enables the desired, comprehensive overall plant performance. Due to the large number of interconnected subsystems and components, complete plants have a high degree of complexity.
Complete systems consist of a number of integrated subsystems and components. Subsystems function with their components as a self-contained unit and form the overall system through interlinking. The more subsystems there are in the overall system, the more complex they are. In plant design, the disciplines listed here can be considered more closely for the classifications. Each of the subsystems has different characteristics and different interrelationships which must be taken into account for each subsystem. For the exact implementation, the plant project design helps. M4 PLANT from CAD Schroer is a comprehensive plant design software. With this software, complex systems can be visualised and designed professionally.
Plant project engineering
Companies in the plant engineering sector develop new plants and manufacture machines according to customer requirements. They also undertake the alteration and modernisation of existing plants and take care of their maintenance over the entire service life of the plant machinery. Plant maintenance is an important point here, because effective maintenance is important to ensure high plant availability.
Automation technology and mechanical engineering are mainly involved with planning work processes that have to be carried out from a proposal phase to the final commissioning of a plant. Plant project planning is preparation for the construction of the actual plant, which is realised by planning processes and other technical procedures. In today’s plant project planning, computer-aided visualisation (e.g. of a CAD model) is used. Project planning usually takes place after the design stage, and a project manager then coordinates the necessary work. The challenge here is to be able to react to changes at short notice. In contrast to design, project planning focuses more on practical implementation. With particularly complex systems, the boundaries between classic project planning and design can become blurred.
Solutions for complete plant engineering
Optimal plant engineering is particularly important for complete plant design. The demands on the software used are high which must support all design disciplines (see examples above). This can only be achieved using multi-disciplinary plant design software, such as the M4 PLANT system from CAD Schroer. This software offers all the tools and modules that are necessary for the modern design and realisation of an industrial plant.
The design is represented in 3D, so that even large factories or plants can be depicted in detail. The user immediately gets an impression of the proportions, the spatial relationships and the required space. This has huge benefits for plant design work.
The M4 PLANT system was developed for the design of plants of any size. Today, it contains various modules for the creation of P&IDs, pipelines, steel structures, heating and air conditioning systems, ventilation systems, the design of conveyor systems and cable routes, as well as for building design. The wide range of design tools provided offers a wealth of possibilities that take every application into account.
Conclusion and summary
Plant engineering is a multi-disciplinary and complex branch of industry without which, as the engine of the economy, many products, services and components would not be realisable. The challenge in plant design is its complexity and versatility. In order to meet this challenge, the project processes needs to be tailored to suit the respective requirements. In addition to the high level of engineering, the project processes are of utmost importance. These processes must be designed in detail and adapted to market conditions. As a result, construction site management is becoming increasingly important in the execution of projects in plant design. Plant project planning helps to ensure precise implementation. M4 PLANT from CAD Schroer is suitable as planning software. With this software, complex plants can be visualised and professionally designed.
FAQ
In plant design, plants are built that consist of equipment and machinery that treat, convert or transport a wide variety of substances. Plants are used in almost every production or operating facility. Together with mechanical engineering, plant engineering is one of the largest industrial sectors in the EU economy. It is involved in the production of many industrial products and is therefore of great importance to industry and the economy.
A plant is, among other things, an energy production or industrial facility that is divided into a structural and a technical plant. It consists of a designed overall system of spatially connected machines or devices that are functionally interconnected to fulfil a specific task.
There are plant manufacturers for every industry that uses machinery and equipment, which includes, for example, the food industry, pharmaceutical industry, construction, aviation, environmental technology, plastics processing, printing, packaging, building materials and the automotive industry.
In plant design there are different disciplines, such as pipeline construction, steel construction, ventilation technology, refrigeration technology, cable route design or building design. These are used differently for the various industries and sectors.
In plant engineering, the focus is on production and manufacturing plants, e.g. food production, robotic systems and vehicle construction, large-scale plants such as sewage treatment plants, chemical plants and power plants. Plant engineers develop processes and then implement them in the form of plants. As a rule, an overall system is created from various technical components, which then fulfil a specific task. Mostly these are plants in process engineering and in energy technology.
In mechanical engineering, one speaks of product development. In such projects, machines are developed, designed and brought into production. In contrast to mechanical engineering, plant engineering is not about product development, but about the emergence of processes and procedures and the combination of existing technical components. Thus, a machine can be a part of a larger plant.
In the EU, machinery and equipment manufacturing is the largest industrial sector in terms of economic output. It accounts for 12 percent of the value added created in the manufacturing sector. In Germany, mechanical and plant engineering is the largest industrial employer and is considered the backbone of the German economy.